Problem: Your WiFi router signal doesn’t reach the whole house, and that needs a solution, because your home office is in one corner and your kids’ space is in the upstairs corner and the SmartTV is in the basement. So what to do if your WiFi router is too far away?
Or maybe your router is in a different room and it can’t be moved, but your main work space is far away.
Solution: If your router is too far from the devices you use, and the WiFi connection is weak or drops frequently, you can opt to wire your device (if it accepts an Ethernet cable and is less than 100 meters away) — or if you really need WiFi, give these troubleshooting steps a try:
8 Simple Steps to Fixing a Weak Router Signal Before Giving Up
- First check the strength of your home WiFi, using a WiFi Analyzer app on your phone and walking around the areas where you need coverage.
- Perform a Speed Test. Go to Fast.com or Speedtest.net to benchmark the speeds you’re actually getting from your ISP. (That being said, don’t do speed tests on wireless to assess your service; if your service is rated for 50 Mbps and you test the speed over your phone, you will not get the same speeds as you would over a wired desktop.) This step should be done before and after changing your router settings to check if each step made a difference.
- Check your Router Settings. Is your signal broadcast strength set too low?
- Check for Router Updates. For a stable and effective network range, you must keep your router’s firmware up-to-date. If your router is running in an old firmware version, then update it to see if that boosts the low signal strength problem.
- Kick Your Neighbours Offline. Limit the number of devices on your network. If your network is currently open (no password), add a password / WPA2 security.
- Place Your Router at Table Height. Routers can be disgusting looking things and your first instinct is to hide it behind your television or in a box. …
- Add another Access Point to your network. You can also use a WiFi Extender to boost the WiFi signal strength of your router.
- Get a Longer-Range Router. Some routers have stronger signals than others. Look on the box to see what range your wireless router is designed to cover.
Router Placement: Distance From Modem
How far can your router be from your modem? Most times, the cable modem and router are happily located right beside each other, connected by a very short length of Cat5e or Cat6 cable. Ideally, you want the shortest distance possible between your incoming service and the network router; less attenuation = more throughput = faster internet.
But consider that your modem is in the basement and you want to place your router closer to your workspace; in this case, you will need a longer Ethernet cable. But how long can you go and not noticeably degrade your internet connection?
- Wired Router: Without experiencing any network interference, the theoretical maximum distance between the modem and router for Cat5e or Cat6 cable is 100 meters or about 328 feet, according to the networking standards.
And how far can a WiFi signal reach?
- WiFi Router: A general rule of thumb in home networking is that WiFi routers operating on the traditional 2.4 GHz band can reach up to 46 meters (150 feet) indoors and 92 meters (300 feet) outdoors. 5 GHz bands reach approximately one-third of these distances, assuming few walls. The main difference between 5GHz and 2.4GHz is signal penetration: 5GHz has a higher attenuation rate as it passes through solid structures. Wall composition also affects your signal levels. In terms of proximity to your modem, ideally you’d want your modem to be within a few feet of your router if not connected directly to it with a cable.
Router Distance from Gaming Computer
Or maybe you’ve noticed that your WiFi connection is terrible for gaming. Maybe you want to use a wired Ethernet connection for better data transfer rates, but you don’t want to drill holes through walls to route your network together.
Ideally you want to use a wired connection for gaming, but what if your router is in the opposite end of the house?
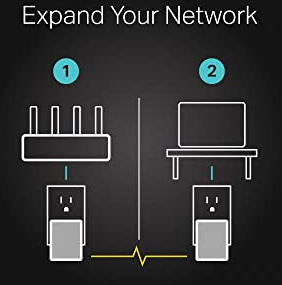
Network expansion: A powerline adapter transforms your home’s existing electrical circuit into a high-speed network with no need for new wires or drilling and brings wired network to anywhere there is a power outlet (up to 300 meters or over 980 feet).
Just plug the powerline adapter into an outlet near your router and connect it to the router via an Ethernet cable. Then in the other room, plug the powerline adapter into an outlet near the device and connect it to the device with an Ethernet cable.
Are Powerline adapters worth it? Powerline adapters are a good way to improve your home network if you want a quick easy fix; they are relatively cheap and require very little technical knowledge to install. They are better than WiFi, in many cases — but if you can, go for a wired connection for best speed, reliability, and efficiency.
How Can I Increase the Range of My Router?
In theory, WiFi signals are capable of passing through walls and other obstacles with relative ease. However, in the real world, walls are of varying thickness or consist of solid concrete and may block some or most of the signals. But standard materials such as drywall, plywood, most types of wood, and glass are easily penetrated by wireless signals. (Keep that in mind if you’re trying to create a protected WiFi-free zone.)
If you have wireless devices like phones and tablets and want to connect them to your network, but the connection to your router is weak, you can simply extend your network with a WiFi extender, or install another Access Point.
Ethernet Cable vs WiFi Signals
- A WiFi connection transmits data via wireless signals, while an Ethernet connection transmits data over cable (a wired connection).
- An Ethernet connection is generally faster than a WiFi connection, and provides greater reliability and security.
- A single run of Ethernet cable is designed to work at a maximum distance of 100 meters, or 328 feet. A length longer than this can result in issues such as dropped packets, reduced performance and loss of signal, particularly when using the older standard Cat5 cable, due to it being limited to 100 Mbps.
- WiFi router signals operating on the traditional 2.4 GHz band can reach up to 46 meters (150 feet) indoors and 92 meters (300 feet) outdoors. 5 GHz bands reach 50 to 100 feet.
How to Boost a WiFi Signal with Aluminum Foil
Aluminum foil has properties that reflect radio frequencies, so it can be used to both strengthen a wireless signal toward one direction, or to prevent the broadcast of a radio frequency in the opposite direction. The foil acts as a reflective yet impermeable broadcasting medium.
Does Aluminum Boost a WiFi Signal?
Radio signals of any type can be affected by metallic objects, including regular household aluminum foil or cans. When applied deliberately, these effects can improve the range of your WiFi router.
If you are looking to increase your WiFi signal in one direction, shape line some cardboard with aluminum foil and shape it into a curved half-circle wide enough to fit around your WiFi router. Place it behind your antenna, with the open end facing the direction you want to increase the signal.

How Does Aluminum Foil Improve a WiFi Signal?
The efficiency of communications on a radio network depends upon the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). This ratio is the strength of the signal you want to receive compared to the signals you are trying to ignore, also known as noise or interference.
Higher SNR translates to better communications with fewer errors.
Think of it like this: if you are sitting in a noisy conference room trying to hear the conversation across the table, you have two ways of improving your SNR. You can change the signal (turn up the volume of the conversation) or turn down the noise (tell everybody to be quiet). Both options are not always possible nor socially acceptable.
Another option is to cup your hands around your ears so as to hear better. This option simultaneously excludes the noise from every direction other than the source of the conversation.
In summary, if your WiFi router and devices are separated by a long distance, placing aluminum reflectors behind your antenna will help to exclude the noise from signals coming from other directions that might be interfering with the signal you are trying to send or receive. If the surface of the reflector is flat and angled correctly, it will reflect back some of the signal that was being transmitted away in a direction that is not useful.
Changing the aluminum or metallic reflectors from flat sheets into parabolic curves will help to focus the signals so that more of the transmitted energy goes in the direction you intend — toward your devices — but only if you are able to place the antennae at the focal point of the parabola. This is the principle used in the design of satellite dishes.
If you do not want to experiment with aluminum cans or foil, another option is to purpose a directional antenna or two.
WiFi Interference and How To Increase Your WiFi Signal Strength
- Place your wireless router on a table, shelf, or mount it on the wall — the higher the better.
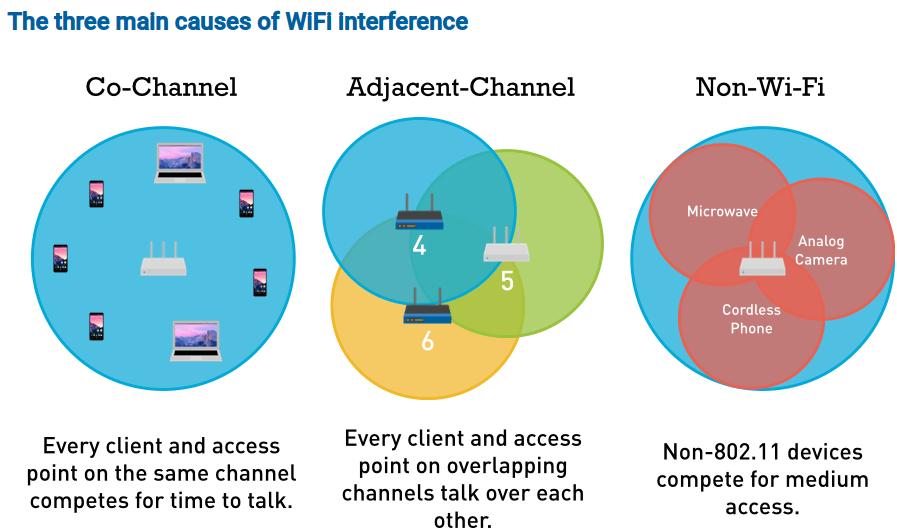
- To improve your wireless range you can also reduce wireless interference; switch the channel your router is broadcasting on, and turn off other devices that use the same band (microwaves, baby monitors, etc. for a 2.4GHz network). In the 2.4 GHz band, 1, 6, and 11 are the only non-overlapping channels. Selecting one or more of these channels is an important part of setting up your network correctly. Currently, many wireless routers automatically select the channel for you upon initial setup, where depending on your wireless environment, it could lead to slow WiFi speeds and interference.
- Reduce the humidity in your home. Humidity interferes with a WiFi signal.
- Utilize metallic shields or aluminum foil strategically to reduce noise and direct the WiFi signal.
- Add another Access Point to your network.
What is a good dBm for WiFi?
If you have been using a WiFi analyzer to monitor the networks in your area, you may notice they are listed according to dBm.
dBm stands for decibels per milliwatt and is a concrete measurement of the power level. It is used to define signal strength in wire and cables at radio and audio frequencies. dBm is measured in very small values and the smaller numbers are the better signal numbers.
For example, -50 dBm is considered an excellent signal strength, -60 dBm is a good signal strength, and -70 dBm is a decently reliable signal strength.
When you are looking at your network, keep in mind that -70 dBm is the minimum for any online services that require a reliable connection and WiFi signal strength.
| Signal Strength | Translation | Required for | |
|---|---|---|---|
| -30 dBm | Amazing | Max achievable signal strength. The client can only be a few feet from the AP to achieve this. Not typical or desirable in the real world. | N/A |
| -67 dBm | Very Good | Minimum signal strength for applications that require very reliable, timely delivery of data packets. | VoIP/VoWiFi, streaming video |
| -70 dBm | Okay | Minimum signal strength for reliable packet delivery. | Email, web |
| -80 dBm | Not Good | Minimum signal strength for basic connectivity. Packet delivery may be unreliable. | N/A |
| -90 dBm | Unusable | Approaching or drowning in the noise floor. Any functionality is highly unlikely. | N/A |
How can I boost my WiFi dBm?
Recall that dBm isn’t a speed measurement, it is a measurement of transmission power. You can increase it only by changing the antenna, if the router has replaceable antennas.