The Domain Name System (DNS) is a global network that connects website domains (URLs) with their IP address. With DNS, it becomes very easy to turn the domain names you type in your web browser into the internet protocol addresses, which computers often connect to.
The DNS server needs to have two servers: Primary DNS and Secondary DNS.
DNS can work alone with the Primary DNS server. However, for the domain name to be readily available at any time, it is best to introduce a Secondary name server.
So what exactly is a secondary DNS server, and when is it used?
A Secondary DNS Server contains backup copies of the primary zone file and can only read information from the zone file — a Secondary DNS Server cannot update or delete records from the zone file it contains; any changes to the zone file have to be made on the Primary DNS Server. Secondary DNS servers offer redundancy or a backup if primary DNS servers are unreachable, offline, or restarting.
A Secondary DNS Server is used to reduce the load on Primary DNS Servers and also for preventing a single point of failure in case the primary server in charge of your domain goes offline.
Zones: What Is A Secondary DNS Zone?
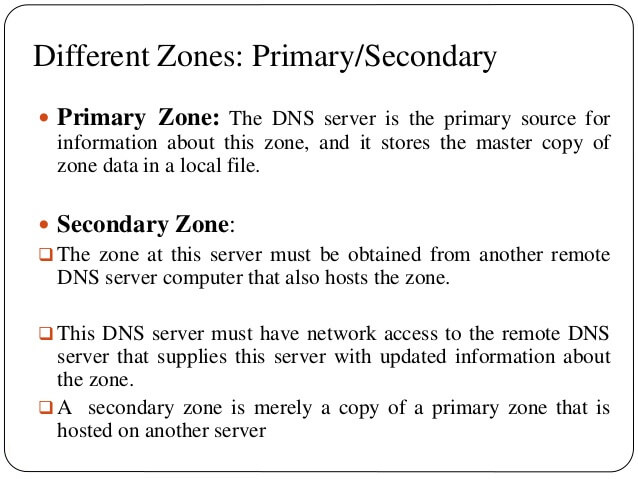
A DNS Zone is a database that contains administrative records for your domain.
DNS Zones are classified into two types: Primary DNS Zone, and a Secondary DNS Zone.
Primary DNS Zone: A Primary DNS Zone is the original read-write authoritative DNS zone or portion of a DNS Namespace. Zone updates are possible only in a Primary DNS zone. The Primary DNS Zone is hosted in the Primary DNS Server.
Secondary DNS Zone: A Secondary DNS Zone is just a Read-Only copy of a Primary Zone, or another Secondary Zone, kept in a Secondary DNS Server. A Secondary DNS Zone is used to reduce the load on Primary DNS Servers and also for preventing single point of failure.
The Zone information from the Primary DNS Server is transferred to the Secondary DNS Server via a process known as Zone Transfer.
When Is Secondary DNS Used?
I mentioned that the secondary DNS server is always up and ready for work and will be in action when the primary DNS server is down or rebooting. So when people visit your site at a time when the primary server is down, instead of them finding it hard to reach your site, the secondary DNS server will keep the website active and allow their browser to resolve your domain.
There are lots of benefits attached to having a secondary DNS server in place to support the master server. Let’s have a quick look at some of them below.
1. Reduced downtime or 100% uptime
One of the benefits of having secondary DNS servers is that it helps to reduce a website’s downtime. As we all know, the secondary server is always up and running, serving as a backup in case your primary DNS server fails. If the Primary DNS provider becomes unavailable, the DNS traffic will automatically be served by the secondary provider without any visible effects to the visitors of the web site.
2. Serves as backup
Related to reducing downtime, the secondary DNS server can also serve as a backup server for the master or primary server. You will have an intact copy of all your DNS records if the primary DNS fails.
3. Provides independency
DDoS attacks are growing in both frequency and severity; adding an additional DNS provider (a Secondary DNS) provides better security and DNS provider independency.
4. Better performance
By using a secondary DNS server, you’ll be able to improve the performance of your system. Instead of directing all the traffic to the primary DNS server, you can always distribute a part of it to your secondary DNS. This will help to reduce the load on the main server, keeping it active and performing properly.
Some organizations, especially high traffic sites that can be heavily affected by any outage, value redundancy to ensure that no one system or service should be responsible for any critical piece of the delivery pathway, including DNS. These web owners might use two or more managed DNS providers and configure nameservers from both for their domains.
Rather than needing to make record changes in the systems of both providers, a common approach is to configure one of the providers as primary and the other as secondary, subservient to the primary provider. Then, all management is done in the primary provider, but both primary and secondary are used for delivery.
5. Other DNS configurations for additional security
If you manage own DNS servers, you can secure them with a Secondary DNS configuration with a hidden Master DNS.
Hidden Primary: Consider the DNS configuration where there is a primary DNS behind the firewall of your company, and you would like to keep it hidden in this way. Your goal is to keep this primary DNS as safe as possible, shielded and unknown to the users. The secondary DNS will be the one exposed to the world, receiving all the updates from the primary. This configuration will not reduce the server load but it is an excellent protection layer for your valuable information.
Difference Between Primary And Secondary DNS Server
The Primary DNS is an authoritative server that is configured to host your website’s primary zone file — a text database file — containing all authoritative information for your domain. The information includes the identity of the domain administrator, its IP address, and resource records.
The primary DNS server is the first point of contact for any device, as well as browsers or applications, interested in translating the human-readable domain name into a numeric IP address.
The main difference between the primary DNS and secondary DNS servers is that the master (primary) server is the one that holds the original copies of all zone records. The secondary DNS server utilizes a special automatic updating mechanism to interact with the master server, ensuring that it maintains a similar copy of data.
For each zone, only a single primary DNS server is available, but the zone can have more than one secondary DNS server.
The master server is responsible for hosting the zone file, which contains all the authoritative information for a domain. The secondary DNS servers offer redundancy when the master server is unreachable.
In terms of data, the primary DNS server gets information directly from local files. When it comes to secondary DNS servers, they only hold read-only copies of the zone file, which gets information directly from the primary server.
Can A DNS Server Be Primary And Secondary For The Same Zone?
For each zone, a DNS server only has a single primary DNS server. However, it can have multiple secondary DNS servers for the same zone. It is possible to have both primary and secondary servers within the primary DNS server of one DNS zone.
Any web server can be used as a DNS server, and any DNS server can be designated as a primary or secondary server. DNS servers can be primary for one DNS zone and secondary for another DNS zone.