WAN is the Internet (wide area network). The WAN port, therefore, is the port that provides connectivity to and from the Internet.
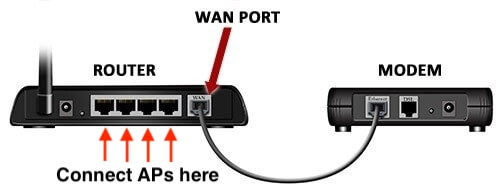
What is a WAN port on a Router?
The WAN (wide area network) port is located on the back of the router. It accepts an Ethernet cable connected to your modem, which brings the Internet service provided by your ISP.
Think of the WAN port as the entry point into your home’s network. It is the front door through which anyone can enter, thus ensure that your home network is WPA2 password-protected.
- WAN is the entry point into your private devices (smart appliances, NAS, server, security system, home automation system or any of your connected computers and phones) from outside your house, from the Public Internet.
- Therefore it is a good security practice to keep your router’s ports closed, use a VPN, or limit your network connection to certain recognized MAC addresses
How to Connect a Modem to a Router: WAN ports and LAN ports
If you are brand new to the Internet, you’ll need to set up your router once your ISP activates your Internet connection. Connecting your modem to your router is the simplest thing in the world. You’ll need two Ethernet cables (Cat 5e or above), your ISP-supplied modem, and your router.
1.Turn off your modem, router and computer.
2.Connect your modem to the WAN port of the router via the Ethernet cable; connect a computer to router’s LAN port via an Ethernet cable.
3.Power on your modem first, then router and computer.
4. Open a browser and type the IP address of the router (most likely it will be 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1). Enter the username and password provided by the router (default username and password is usually admin or left blank).
5. Set up your home network: provide a name for your network, enable WPA2 key security, and provide a password. And then click finish.
6. Now restart your router — and, your network should be live! (You can now disconnect the Ethernet cable from your computer to your router if you are connecting via WiFi to the router’s network SSID.)
WAN port vs LAN port
The job of a home router is to create a private network on the LAN (local area network). If the router box includes an Access Point (in which case the device is usually called a WiFi router), then the router will also issue an SSID for WiFi, in addition to assigning IP addresses to devices on the LAN, and routing traffic between your private network and the public Internet on the WAN side.
- WAN is mostly synonymous the the Internet
- The LAN port is for your home network.
- The WAN port is used to connect a LAN (your home network or other private network) to an external network (usually an ISP server) which can forward your data requests to the outside world (the Internet).
WAN port vs DSL port
There are two types of home router: those with a modem built-in and those without. Modems are for connecting to a specific type of broadband Internet service, usually either over phone line (DSL) or cable (or increasingly, fibre optic cable).
If you subscribe to a DSL Internet service, you will receive Internet access through a phone line. On a home broadband router, the DSL port is for connecting your Internet service to your home through a phone line (as opposed to a coaxial cable line for cable Internet service).
- Routers with built-in modems connect directly to the phone line via a DSL port on the router.
- Routers without a built-in modem require a separate modem to connect to your broadband service, and so these routers have WAN ports for connecting to this modem via an Ethernet cable.
Some routers have both a built-in modem and a WAN port; the WAN port in this case is provided so that you can use the router with an external modem instead of the built-in one (not usually at the same time). This is useful if you change your broadband service in the future to one requiring a different modem, and you still want to continue using the same router.
How to Use the WAN port on a Router
Do I plug Ethernet into WAN or LAN? If you are extending your Internet service from your modem to a router, plug the Ethernet cable from your modem into the WAN port of your router.
- LAN is your Local Area Network and describes the network of your home devices: small switches, printers, media servers, and other computers are all connected to each other via your LAN, which assigns each device a unique IP address on the local network. If you are connecting a computer to your network router via Ethernet, then you would connect the Ethernet cable to a LAN port of the router and the RJ45/Ethernet port of your computer.
- WAN or Wide Area Network is generally the term used to describe your connection to the WAN or Internet, via ADSL/VDSL/DSL, Fibre, cable, or even dial-up service.
So, a WAN cable is the same as an Ethernet cable, but to improve your network performance, choose the minimum Cat5e cable (or Cat6) length required to connect your modem to your router. If your router is a long distance from your modem, just don’t go over 100 meters away with a length of Cat5e cable and your signal should be fine.
Question: I have two routers. What is the WAN port for in this setup, and how do I extend my home network?
In this setup of two routers, the WAN port is for connecting your second router to a LAN port of the main router, switch, or modem. Be sure to properly configure your router to use a different IP range before attempting to extend your network.
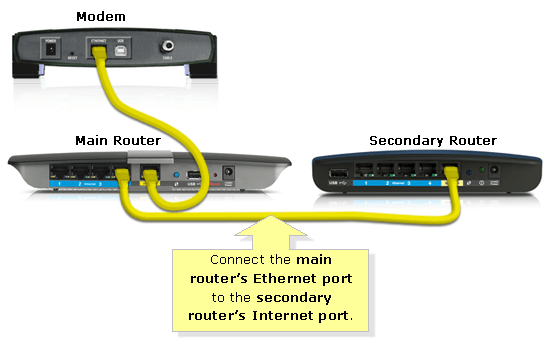
You will also want to set up static routing on the second router to avoid duplicate NAT (IP address interference).
- For instance, consider the situation in which your existing modem and router are working, and the router is operating the network range 192.168.0.1 – 192.168.0.254 (.0 and .255 are reserved for listen and broadcast on devices in the range for the default netmask 255.255.255.0).
- If you want to add the second router, configure the second router to operate in the range of 192.168.1.1 – 192.168.1.254 (change just the third octet) in its LAN settings. Log into your router to change the settings. For WAN settings, leave it as DHCP (unless you require port forwarding to work all the way down, in which case, configure it for Static IP in WAN settings).
- Now save all changes, and reboot the router to effect the changes. (Your device that you are using to make the changes should disconnect while the router reboots, then reconnect).
- Now connect an Ethernet cable to both the WAN port of the second router (192.168.1.1) and any open LAN port of the first router.
Convert a LAN Port into a WAN Port
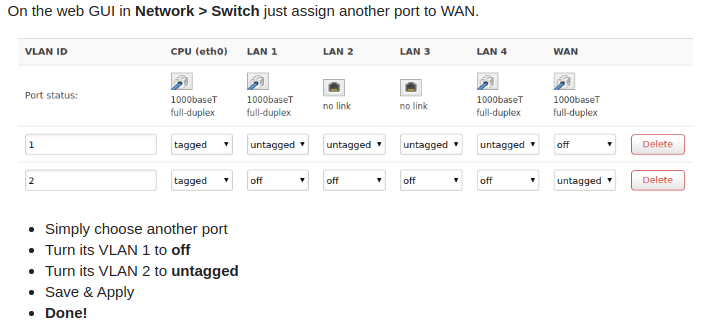
If your WAN port was physically damaged but your router’s LAN ports are okay, you might want to make one of your LAN ports into a WAN port instead of throwing your router out or repurposing it as a switch.
To do this, download OpenWrt (first check if your router is compatible with the firmware). If the other ports are working, you can reconfigure the switch using LuCI. Take note of the settings of the WAN port in the switch-configuration section, copy them to the port you want to use, and remove all settings from the “old” WAN port.
Related: here’s how to configure the network of a GL-AR750 device, using OpenWRT, in order to use a LAN port as your second WAN, so that afterwards you can configure Mwan3 to load balance Wan connections.