The term “embedded systems” is usually used to describe the devices or machines that operate with minimum or no human supervision. Probably any device that runs software can be called an embedded system to some extent. Think of your dishwasher, microwave, washing machine, or oven: these devices arrive with a computer board that is pre-programmed and requires no updating.
An embedded system is a computer with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system. They often perform pre-defined tasks with very specific requirements. The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnected network of these physical devices.
IoT (Internet of Things) and embedded systems are both related to the integration of computing and communication capabilities into everyday objects and devices. However, there are some key differences between the two:
- Embedded systems are computer systems that are integrated into other devices or products, typically for a specific function or set of functions. These systems are designed to perform a specific task within a larger system, and they are often found in devices that are not primarily computers, such as automobiles, industrial machines, medical devices, and other types of equipment. Embedded systems typically include both hardware and software components, and they may be connected to other devices or systems within a local network. Unlike general-purpose computers, which are designed to be flexible and can run a wide range of applications, embedded systems are specialized and optimized for a specific function or set of functions.
- The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnected network of these physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other objects that are equipped with sensors, software, and network connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data. The IoT enables these connected devices to communicate and interact with each other and with external systems, allowing for the automation of many tasks and processes.
Difference in Scope Between Embedded Systems and IoT
IoT (Internet of Things) refers to the interconnected network of devices that are connected to the internet and can communicate with each other. These devices can include a wide range of appliances and devices, from smartphones and laptops to smart thermostats and security cameras. The scope of IoT is broad and encompasses a wide range of devices and applications.
Embedded systems, on the other hand, refer specifically to the use of computing and communication capabilities in devices that are not primarily computers. These devices can include automobiles, industrial machines, medical devices, and other types of equipment.
The scope of embedded systems is generally more narrow and specialized than IoT.
Difference in Purpose of Embedded Systems versus IoT
The primary purpose of IoT devices is to collect and transmit data over the internet, often for the purpose of automation or remote control.
For example, a smart thermostat might be connected to the internet and able to communicate with a smartphone app, allowing you to adjust the temperature of your home remotely. An IoT security camera might be able to send alerts to your phone if it detects motion or other unusual activity.
Embedded systems, on the other hand, are designed to perform a specific function or set of functions within a larger system.
For example, an embedded system in a car might be responsible for controlling the engine, while an embedded system in a washing machine might be responsible for controlling the wash cycle.
The purpose of an embedded system is typically to perform a specific task or function, rather than to transmit data or communicate with other devices.
Difference in Complexity Between Embedded Systems and IoT
Because IoT devices are designed to be used by a wide range of people with varying levels of technical expertise, they tend to be simpler and more user-friendly than embedded systems. IoT devices are often designed to be easy to set up and use, with intuitive interfaces and clear instructions.
Embedded systems, on the other hand, are often designed for use by trained technicians or engineers and may be more complex and specialized in their capabilities.
Embedded systems may require a higher level of technical expertise to set up and maintain, and they may include a wider range of features and capabilities than IoT devices.
Connectivity Differences Between Embedded Systems and IoT
One of the key differences between IoT and embedded systems is their level of connectivity.
IoT devices are designed to be connected to the internet and to communicate with other devices over the internet, using technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular connectivity. This allows IoT devices to be accessed and controlled remotely, and to transmit data to and from other devices and systems.
Embedded systems, on the other hand, may or may not have internet connectivity. Some embedded systems may be connected to other devices or systems within a local network, but they may not have direct access to the internet. This means that embedded systems may be more limited in their ability to communicate with other devices or systems, and they may not be able to transmit data to or from the internet.

IoT is an integration that can have many connectivity options and devices; however, IoT has nothing to do with technical specifications. IoT includes embedded technology, network technology, and information technology. Embedded systems can become part of the IoT infrastructure when you connect them to network technology and information technology infrastructure. IoT can be constantly programmatically updated according to the environment.
How does IoT relate to embedded systems?
Most Internet of Things (IoT) products are in fact embedded devices which are connected to the internet. IoT fans imagine a world where the internet and cloud resources process huge amounts of data collected by these devices, and use it to improve the services and devices.
With the growth of IoT, micro-controller firmware engineers, who specialize in C programming, know some assembly languages, and are adept at designing simple devices, will be in high demand.
Embedded systems are a type of device that is typically found within the larger category of the Internet of Things (IoT). These systems are characterized by small software programs that are designed to perform specific functions within a larger system. To be considered part of the IoT, a device must be connected to the internet and equipped with sensors, processors, software systems, and protocols that allow it to communicate with other devices and systems. Web APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) can also be used to enable communication and integration between different devices and systems within the IoT.
IoT systems overview
The Internet of Things describes a mass of sensors, computers, and network connections designed into objects (embedded systems) so that they can be centrally controlled. This technology has a huge potential, as its efficiency creates significant economic value. The Internet of Things is the opportunity to update and configure the functionality of the devices through the cloud platform.
Smart homes are one manifestation of the IoT. With one click of a button, or one tap of an icon, you can control your lighting, thermostat, alarm clock, and other devices connected to an app on your smartphone.
You may have a smart home speaker, for example, which helps you to control some other connected devices in your home with just the sound of your voice.
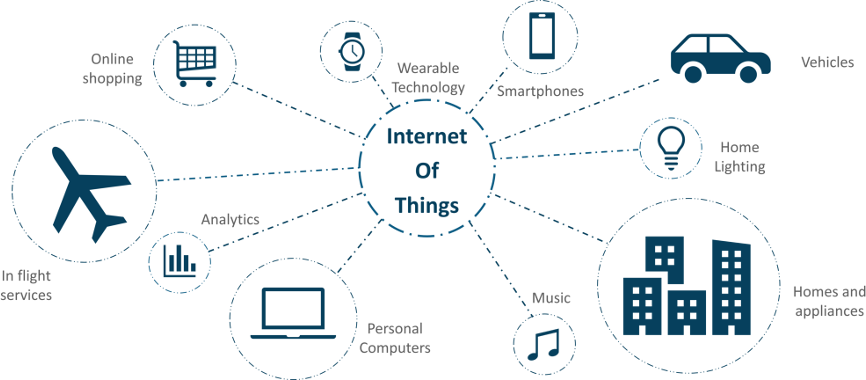
The IoT is great, but with its conveniences come many risks. Having devices monitoring the environment poses many concerns: the invasion of privacy and potential risks of getting your devices hacked and controlled by third parties, or having your data harvested by the manufacturers of such devices.
So, basically, IoT is a network of objects that are connected to the internet, and through the internet, an embedded system is able to collect and exchange data. Internet of Things works through the embedded applications that can be used to control and monitor your other devices from anywhere.
Embedded systems overview
Embedded systems are hardware and software programs that are embedded into everyday things. These programs are set to perform certain functions which can not be updated once the system is shipped to the customer. Embedded systems can be found in every house in washing machines, routers, modems, microwave ovens, toaster ovens, and dishwashers.
Embedded systems are a combination of customized hardware and software that performs one specific task.
Customized hardware is a specific design that suits the system and has a particular set of requirements.
Customized software is a developed program that performs the desired function. Embedded systems are limited in terms of resources, as they have lesser computing power, memory, and peripherals.
Embedded systems have unique features and characteristics like low power consumption, real-time computing, high availability, which makes them very important for developing IoT technology. Embedded systems are key enablers of the Internet of Things.
As a good example, think of your mobile phone. This model has specific hardware like storage space, screen type, camera pixels, etc. The software requirements depend on the hardware capability. The brand of the phone releases a new update. For other models of phone, this update is applicable, but for this one – it is not.
This is the nature of embedded systems. There are embedded boards that support different controllers developed using software and hardware units. Embedded systems cab be microprocessors that are are usually a part of a bigger device where they have a certain function to perform in the device.
Difference between IoT and embedded systems
The Internet of Things products can be used for home automation, and the embedded systems are within the products networked together to automate and control air conditioning, heating, etc.
Think of an embedded system as any electronic device that assists you in solving a specific problem:
- mobile phones
- microwaves
- coffee machines
- fridges
- air conditioning
- traffic lights
- remote controls
These computer-integrated products are all examples of embedded systems. There are many embedded systems in cars , such as airbags, anti-lock brakes, and SatNav systems.
Embedded systems are usually small software programs with few functions, embedded into the item, and that can not be changed once the item leaves the factory. An embedded system can be linked to the Internet of Things if it has been programmed to connect to the internet.
The Internet of Things is now the most trending technology because we can control our devices from anywhere using this technology. With the help of certain sensors, actuators, processors, software systems, web APIs, the Internet of Things creates a connected environment of embedded systems.
Embedded systems and IoT usually work together: while IoT connects a set of embedded devices, these embedded devices with sensors collect and exchange data regarding the changes in device and capturing relevant data, such as sound, motion, temperature, etc. This data is sent via the internet to a smartphone that has an internet connection.
The Internet of Things means implementing everything in the cloud, which makes it more complex than an embedded system. The Internet of Things may have access to bid data, while an embedded system does not. Embedded systems do not introduce privacy and security concerns into devices because they are not able to transmit data on their own.
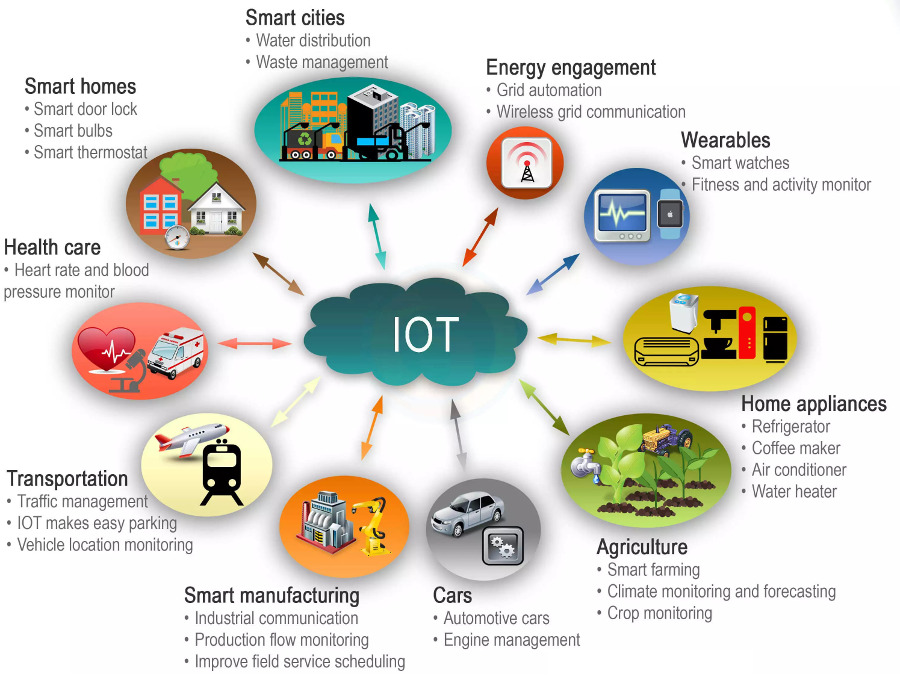
With the advancement of wireless communication, the devices will be able to connect to each other seamlessly. The future of IoT and embedded systems depends on the improvement of the technologies for faster communication with high intertwined connections between devices.
IoT is getting more and more popular in our daily lives, so this technology’s advancement is inevitable and can be definitely expected to continue. This can pose some problems with privacy and security, which will require new solutions and improvements of the system security of internet-connected embedded systems.